
Skills for Success
Want to know what it takes to get back to work? Learn about the skills needed to participate and thrive in learning, work, and life! The Government of Canada’s Office of Skills for Success (OSS) has launched a renewed skills model – Skills for Success (SFS), that provides modernized support to Canadians for upskilling/reskilling and will support them in getting back to work. The renewed model is flexible for different learning, work and life contexts.
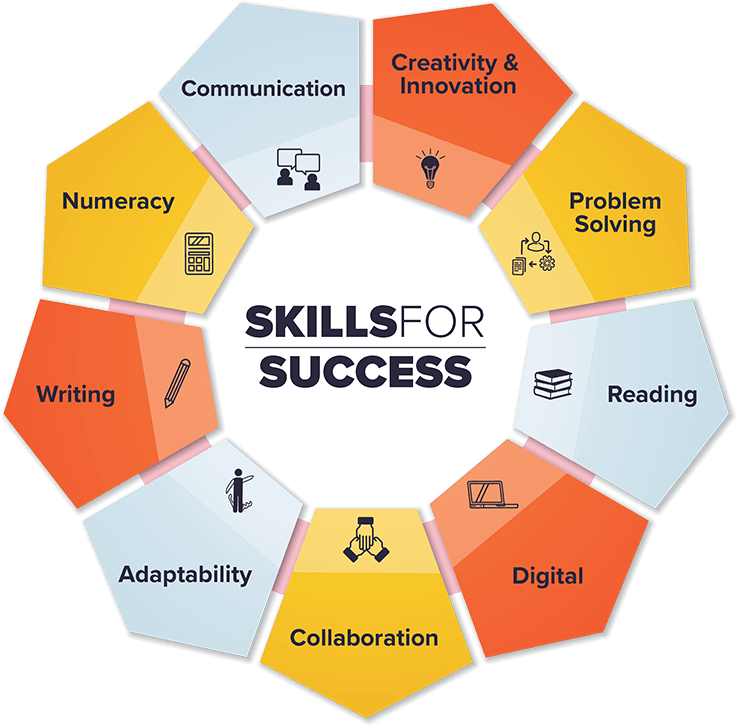
Skills for Success are the foundational and transferable skills needed to participate and thrive in learning, work and life. The circular model illustrates that each skill is just as important as the other, and they all contribute to the success of Canadian workers.
Skills for Success includes skills that are needed for building new skills and knowledge and are important for effective social interaction. These skills can overlap and interact with each other, and with other technical and life skills. They are inclusive and can be adapted to different contexts.
Skills for Success are for everyone – employers, workers, training providers, governments, and communities. They are critical to Canada’s economic and social prosperity.
Unlock Your Potential in Work and Life
Skills For Success

ADAPTABILITY
Is the ability to achieve or adjust goals and behaviours when expected or unexpected change occurs, by planning, staying focused, persisting, and overcoming setbacks. For example, we use this skill to change work plans to meet new deadlines, learn how to work with new tools and improve our skills through feedback.

Collaboration
Is the ability to contribute to and support others to achieve a common goal. For example, at work, we utilize this skill to offer meaningful support to team members while they complete a project.

Communication
Is the ability to receive, understand, consider, and share information and ideas through speaking, listening, and interacting with others. For example, we use this skill to listen to instructions, serve customers and discuss ideas.

Creativity and innovation
Is the ability to imagine, develop, express, encourage, and apply ideas in ways that are novel, unexpected, or challenge existing methods and norms. For example, we use this skill to discover better ways of doing things, develop new products, and deliver services in a new way.

digital
Your ability to use digital technology and tools to find, manage, apply, create and share information and content. For example, we use this skill to create spreadsheets, safely use social media, and securely make online purchases.

numeracy
The modern economy requires numeracy skills that go beyond basic arithmetic. Understanding numbers remains critical to functioning in today’s society. Many jobs require the ability to work with numbers and math.

Problem solving
Your ability to identify, analyze, propose solutions, and make decisions. Problem-solving helps you address issues, monitor progress, and learn from the experience. For example, we use this skill to make hiring decisions, select courses of action and troubleshoot technical failures.

reading & writing
Reading helps you to understand and interpret the meaning within the text. Strong reading skills allow you to do your job and to work safely and efficiently. We require Writing skills that are suitable for different situations, including digital platforms.
Resources
Find programs near you:
UNESCO Literacy
Literacy involves a continuum of learning that enables an individual to achieve their goals, develop their knowledge and potential, and participate fully in the wider society.
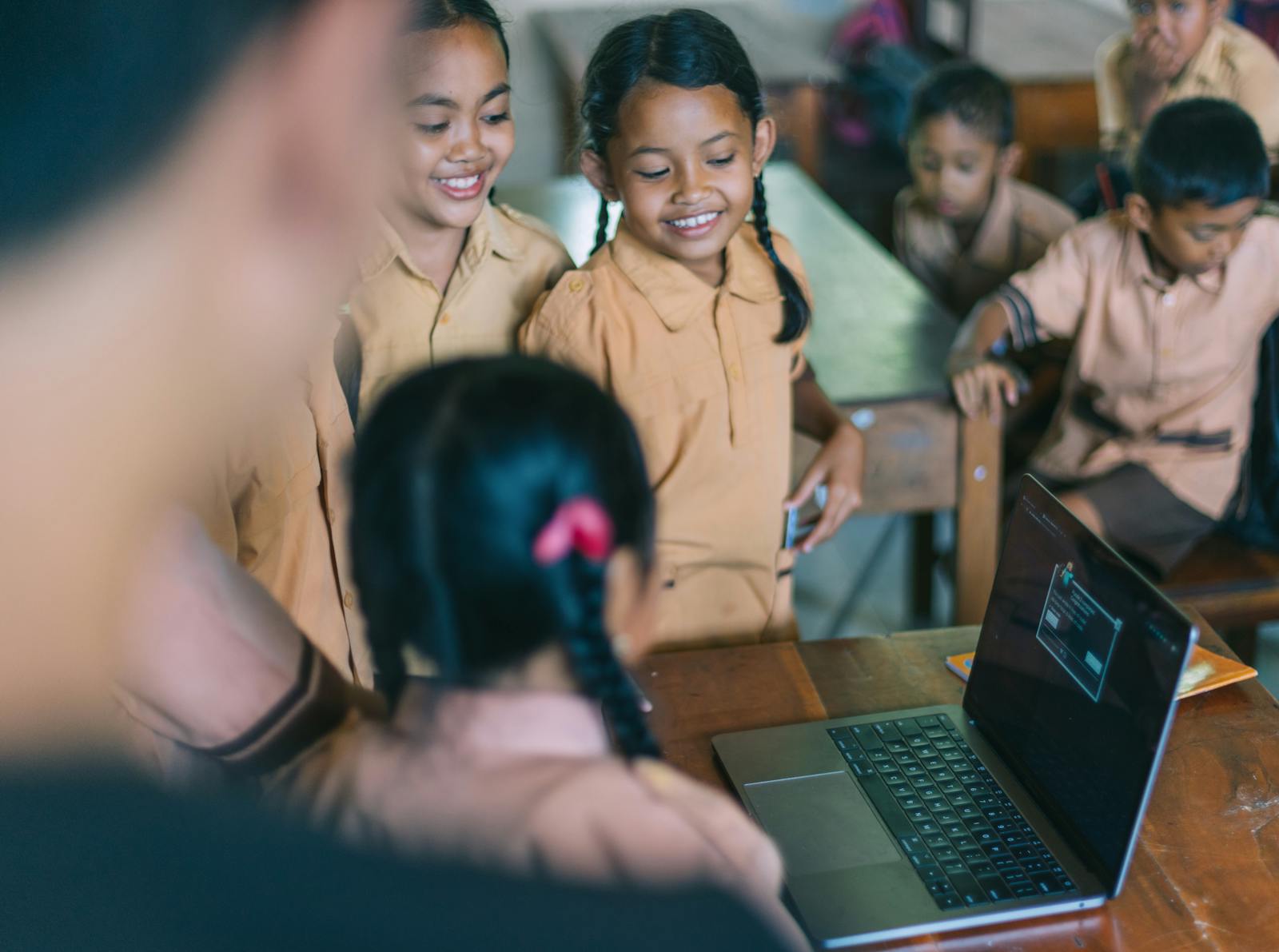

Despite the steady rise in literacy rates over the past 50 years, there are still 754 million illiterate adults around the world, most of whom are women. These numbers produced by the UIS are a stark reminder of the work ahead to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially Target 4.6 to ensure that all youth and most adults achieve literacy and numeracy by 2030
Visit UNESCO’s Education and Literacy Statistics page to find out more.
